The login pages of a web site are usually HTML forms. The HTML forms will be linked to a script to process the data received via form from the user. This linking is performed by HTM Form Attribute called “Action” (HTML <form> action Attribute).
Syntax: <form action="<scriptname>" method="<post/get>">
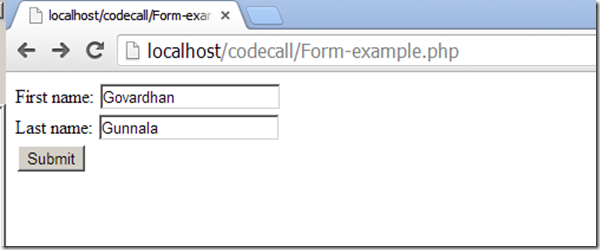
Example: Save below content as “Form-Example.php”
<form action="login.php" method="post">
First name: <input type="text" name="fname"><br>
Last name: <input type="text" name="lname"><br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form>
The page would look like below form for the end user:
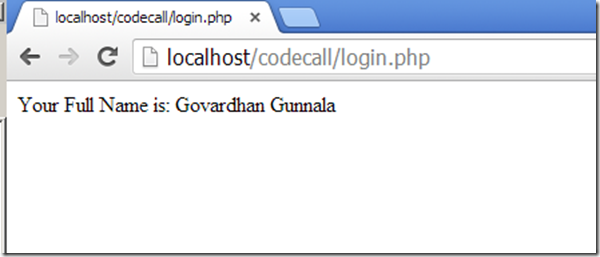
Upon user clicks “Submit” button the respective login.php script gets invoked. Let’s say you’ve setup login.php as below:
<?php
if( $_POST[‘fname’] && $_POST[‘lname’] ) {
echo "Your Full Name is: ", $_POST[‘fname’], " ", $_POST[‘lname’];
} else {
echo "You have not mentioned either First or Last name, please try again!";
}
?>
The output would look like below for the end user:
The important notes about HTML Form Action attribute:
- If you leave the action attribute blank or without any script location, then it’s simply reloads the form page again.
<form action="" method="post">
- The page will be self posted back to itself if it’s action attribute is:
- not specified, i.e., “action=” is omitted
- is set to nothing, above case
- is set to # i.e., “action=#”