Certificate Requirements for Setting up AD FS
During my recent evaluation of AD FS, I have gone through various articles but there wasn’t any clear mention or details about how the certificates be configured for AD FS. Here is my attempt to share all of my learning and how I got it setup working. I found the relevant MS article after I got whole of my setup done, it doesn’t show up in the search results 🙁
Environment:
- Windows Server 2012
- AD FS 3.0 (which comes as default in server 2012 OS)
- Domain Functional Level: Windows Server 2008 R2
- AD FS installation on the Domain Controller (since its my test lab)
Requirement:
- AD FS is a secured service for which it needs a Server Certificate to establish SSL communication with the clients. During AD FS installation you’ll be prompted to provide a certificate as shown below:
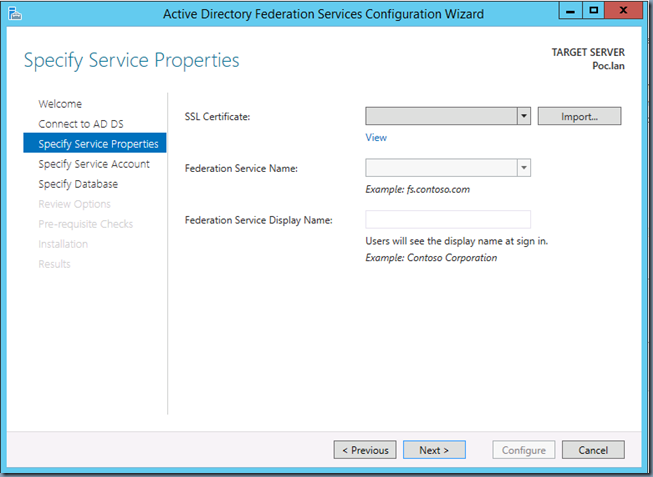
- Say I want to name my AD FS Single Sign-on service as fs.poc.lan for this you’ll need a certificate issued for fs.poc.lan
Installing Enterprise CA for Ad FS:
For setting up the internal certificate for the ADFS server, you can setup an Enterprise CA in your lab. This generated certificate will be used for ADFS installation.
- You can install the Enterprise CA on a AD Domain Controller server that is running with DataCentre edition of Windows
- Standalone CA on a Windows Standard edition would require more manual configuration efforts and may delay your lab setup
- You need to be member of the “Enterprise Admins” group in the domain you are setting it up for
Configuring Certificates for Ad FS:
SSL Server Authentication Certificate
You need to obtain an SSL certificate from a trusted third party vendor (godaddy or verisign, etc.,) and install it on your production instance so that your clients will be able to verify the trust of your server certificate from anywhere.
For the purpose of example, I’ll be using my locally installed Enterprise CA issued server certificate here. However, in either case this server certificate should support below specifications.
- Subject name or subject alternative name must contain the exact name of your federation service such as fs.poc.lan or a matching wildcard expression such as *.poc.lan
- Example:
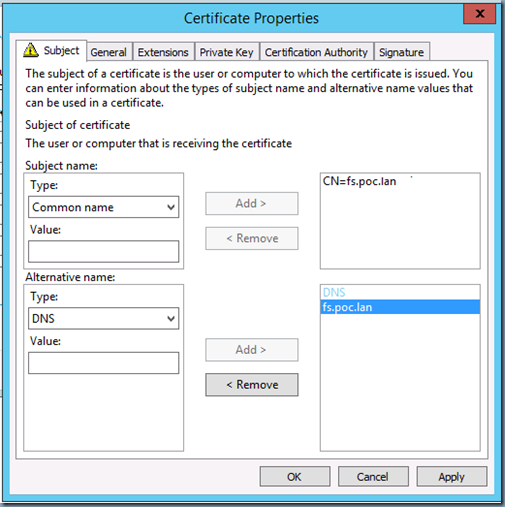
- If your organization uses multiple UPN suffixes, the SSL certificate must contain a subject alternative name entry for each suffix. Say you have sub-domains and would like uses be able to authenticate using both username@domain.com and username@sub.domain.com. In which case your certificate should be valid for both the main domain and the sub-domain names.
Token signing and token decryption certificate:
AD FS configuration wizard takes care of it by default. A token-signing certificate and a token decryption certificate are created automatically during the AD FS installation and do not have to be provided by the administrator.
However, one can setup their own CA issued or third party issued certificates for token-signing and token decryption via PowerShell and NOT using the AD FS wizard.
Service Communications Certificate:
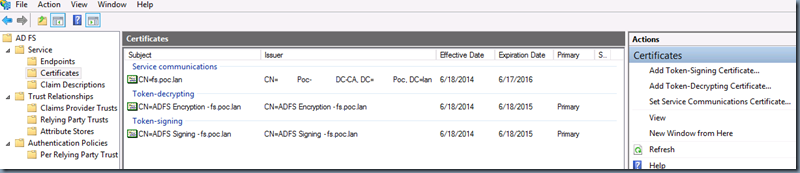
Please do NOT confuse this with above explained Server Certificate. This certificate is distinct from the SSL certificate of the federation server. This certificate is used for scenarios that require message security. However, By default, the initial AD FS configuration assigns the certificate that the administrator provides as the SSL certificate to the service communications certificate role. This can be changed after initial AD FS configuration by using the AD FS Management snap-in. To manage the Service Communications Certificate, use the AD FS Management snap-in as shown below.
Viewing/Finding/Managing the AD FS certificates from AD FS Management Console:
- From Server Manager > Tools > AD FS Management
- In AD FS Management > AD FS > Service > Certificates.
Reference: